Conventional hybrids combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor, but they are not primarily fueled by electricity. The battery is charged through regenerative braking, which captures energy and converts it into electricity during braking. They do not utilize plug-in charging and are not included as part of the Collaborative.
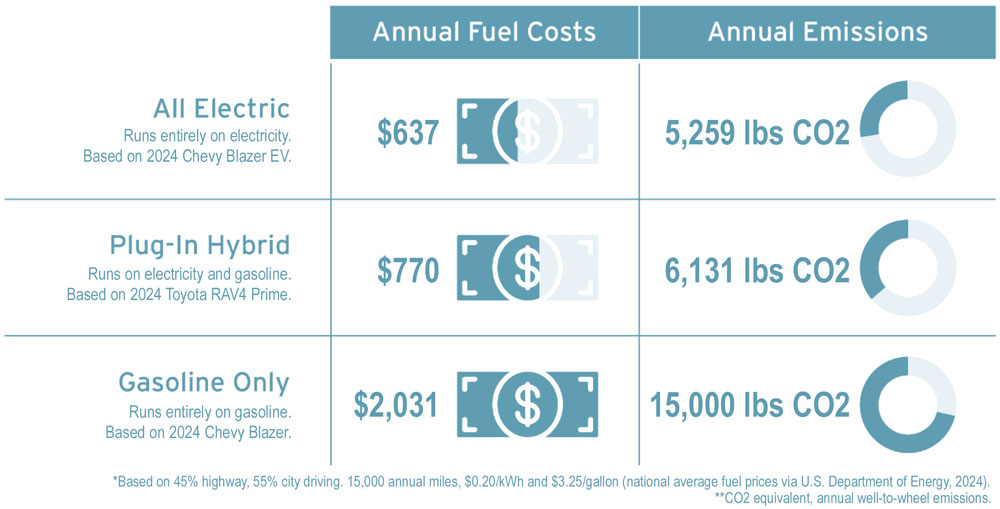
The two primary types of plug-in electric vehicles are battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). PHEVs, similar to conventional hybrids, are made up of an internal combustion engine and an electric motor. However, PHEV batteries can be charged by plugging into an outlet, providing the vehicle a limited electric range. When the battery is depleted, the internal combustion engine takes over. BEVs only utilize an electric motor and run solely on electricity from the grid by plugging into an outlet or charging station, replacing gasoline entirely.